Overview
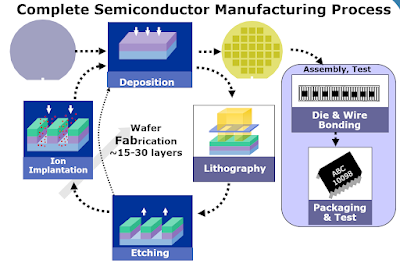
Microchips such as CPUs, GPUs are baked from silicon wafers as shown in the process flow below.
As time and technology advanced, also while trying to keep up with Moore's law,
- The size of the wafer has increased from 50 mm in late 1960s to 300 mm in the current foundries at intel, samsung etc.
- The number of transistors in a chip and its clock speed has increased from 1 million/25 MHz in early 1990s to 20 billion/5 GHz in current times.
- The number of CPU cores has gone up from 1 to 5 with the bonus of hyper threading.
- Also worth noting that GPUs now have 1000+ cores.
As the software applications are getting complex, monolithic. single threaded architecture is no longer relevant. Multi threaded architectures with parallelism features is the trend.
Modern Operating systems such as Windows are geared up to harness this tremendous processing power to make it available to user applications. Windows OS, is a multiprocessing, multitasking, multi threaded, preemptive, multiuser operating system. It provides kernel objects for multi threading and synchronization among user applications. It also provides thread pooling. timer service and other facilities. User applications can avail these features using Win32 SDK.
Details
Standard library concurrency objects can be broadly classified into five categories.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Execution Class and functions | Execute code asynchronously and results are stored in Execution Utility Classes. |
| Execution Utility Classes | Provide mechanism to store results and exceptions later to be retrieved asynchronously. |
| Synchronization class and functions | Provides synchronization between Execution Classes by Conditionally blocking execution of code and unblock in a thread. The usage can vary from protecting a resource to prevent race conditions. |
| Synchronization Wrapper classes and functions | Provide wrapper for Synchronization classes, to help with their construction and destruction. |
| Lock free programming | Provide interlocked atomic operations using Atomic class. |
The following describes synchronization object for each category.
Execution Classes and functions
These classes can execute code asynchronously.
The following describes synchronization object for each category
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| async()➹ | Same as Win32 thread pool - enables running short tasks in a dedicated thread pool. |
| thread➹ | Same as Win32 thread - An independent unit of execution. |
| this_thread➹ | Provides functions that access the current thread. |
| packaged_task➹ | Similar to async except it can be launched at a later time. |
Execution Utility Classes
These classes store the result or exception to be retrieved asynchronously.
The following describes synchronization object for each category
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| promise➹ | Template class that is used for storing the result or exception of the thread function in a shared state. |
| future➹ | future object can access shared state in the promise object containing the result or an exception. It's a single use object. |
| shared_future➹ | Similar to future object except multiple threads are allowed to wait for the same shared state. |
Synchronization Classes and functions
These classes provide synchronization between Execution Classes.
The following describes synchronization object for each category
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutex➹ | Provides synchronization to access to a shared resource from multiple threads. |
| timed_mutex➹ | Same as mutex. It also extends locking for a duration or timepoint. |
| recursive_mutex➹ | same as mutex$ except owning thread can call lock() more than once recursively. |
| recursive_timed_mutex➹ | A recursive and timed mutex. |
| conditional variable➹ conditional variable_any➹ | Same as Win32 conditional variable - Designed to address producer/consumer scenario. |
| call_once()➹ | Same as Win32 InitOnce - One time initialization of variables that's used in multiple threads. |
Synchronization Wrapper Classes and Functions
These classes provide wrapper for Synchronization classes.
The following describes synchronization object for each category
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| lock_guard➹ | A RAII-style object for owning a mutex for the duration of a scoped block. |
| unique_lock➹ | Similar to lock_guard with extended functionality allowing deferred locking, time-constrained attempts at locking, recursive locking, transfer of lock ownership, and use with condition variables. |
| shared_lock➹ | Similar to unique_lock except it can use other lockable types. |
| lock()➹ | Enables locking multiple mutexes without deadlocking |
Lock free programming
The synchronization mechanisms discussed earlier uses operating system provided objects using atomic classes which provide interlocked atomic operations..
The following describes synchronization object for each category
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| atomic➹ | Same as Win32 interlocked - provide a large range of atomic operations. |
| atomic_flag➹ | Same as atomic<> for boolean - guaranteed to be lock free. |
Summary of Examples
In wandbox and GDBOnline examples can be viewed, edited, built and run.
| Name | Synchronization Object | Github | Wandbox |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example | promise - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 2 | promise - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 3 | future - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 4 | shared future - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 5 | async - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 6 | thread - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 7 | thread - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 8 | packaged_task - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 9 | this_thread - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 10 | mutex - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 11 | timed_mutex - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 12 | recursive_mutex - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 13 | unique_lock - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 14 | lock - (usage) restaurant | source output | source+output |
| Example 15 | lock - (usage) bank | source output | source+output |
| Example 16 | call_once - (usage) async | source output | source+output |
| Example 17 | call_once - (usage) thread | source output | source+output |
| Example 18 | conditional_variable - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 19 | conditional_variable - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 20 | atomic<> - functionality | source output | source+output |
| Example 21 | atomic<> - usage | source output | source+output |
| Example 22 | atomic_flag - functionality | source output | source+output |
No comments:
Post a Comment