The standard library provides valarray class is similar to a vector but mathematical functions can be applied directly to all the elements. It also allows to get different cross section of the elements in the valarray including multidimensional using helper classes.
Details
The overloaded [] operator of valarray allows enables extraction and manipulation of its elements in different cross section using a set of helper classes listed below.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| slice | A definition to a single dimension collection of elements to a valarray. |
| slice_array | A collection of elements in the valarray referred by the slice. |
| gslice | A definition to a multi dimension collection of elements to a valarray. |
| gslice_array | A collection of elements in the valarray referred by the slice. |
| mask_array | A valarray<bool> object that refers to individual elements in a valarray. |
| indirect_array | A valarray<size_t> object that contain indices to individual elements in a valarray. |
The following discusses each of these in detail.
slice
slice class represents a valarray slice selector similar to BLAS slice. It does not contain nor refers to any element - it only describes a selection of elements to be used as an index in valarray::operator[].
A slice is defined by the following:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start | index of the first element in the selection. |
| size | number of elements in the selection. |
| stride | span that separates the elements selected. |
The elements in a slice are computed as below.
(start + 0 * stride), (start + 1 * stride), ..., (start + (size - 1) * stride).
slice class defines following members.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| slice(size_t start, size_t size, size_t stride) | Constructor |
| size_t start() | returns start. |
| size_t size() | returns size. |
| size_t stride() | returns stride. |
slice_array
Represents an intermediate type returned by valarray's subscript operator (operator[]) when used with slices.
It references the elements in the valarray object that are selected by the slice, and overloads the assignment and compound assignment operators, allowing direct access to the elements in the selection.
The type is convertible to a valarray, producing a new object with copies of the referred elements.
The following members are defined.
template <class T> class slice_array { public: typedef T value_type; void operator= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator*= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator/= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator%= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator+= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator-= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator^= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator&= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator|= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator<<= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator>>= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator=(const T&) const; slice_array() = delete; slice_array(const slice_array&); const slice_array& operator= (const slice_array&) const; ~slice_array(); };
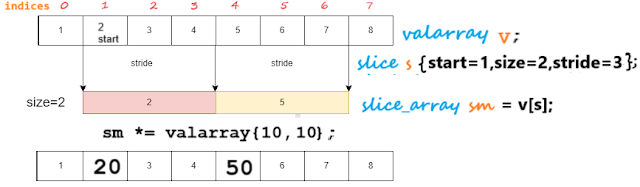
The following diagram depicts slice and slice_array pictorially.
The following examples demonstrates getting diagonal elements in a 3x3 matrix.
valarray<int> m {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; //diag:{1,5,9} auto diag = valarray(m[slice(0,3,4)]);
gslice
gslice class represents a valarray generalized slice selector (a multidimensional slice). It does not contain nor refers to any element - it only describes a selection of elements to be used as an index in valarray::operator[].
A gslice is defined by the following :
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start | index of the first element in the selection. |
| size | an array that defines the number of elements in each dimension |
| stride | an array that defines the number of positions between successive elements in each dimension |
The elements in a slice are computed as kj=s+Σj(ijdj).
where s is starting point, ij is list of strides, dj is list of lengths.
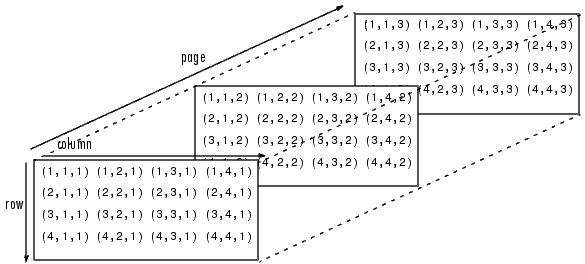
For example, consider the following 3D matrix.
Suppose we want to extract all the diagonal elements in all the three pages, a gslice with
start = 0, strides = {16,16,5} and lengths = {3,1,4} can be used.
As shown below, the matrix represents 12 (3*1*4) diagonal elements. They are computed as below:
0 + 0*16 + 0*16 + 0*5( 0), 0 + 0*16 + 0*16 + 1*5( 5), 0 + 0*16 + 0*16 + 2*5(10), 0 + 0*16 + 0*16 + 3*5(15)
0 + 0*16 + 1*16 + 0*5(16), 0 + 0*16 + 1*16 + 1*5(21), 0 + 0*16 + 1*16 + 2*5(26), 0 + 0*16 + 1*16 + 3*5(31)
0 + 1*16 + 1*16 + 0*5(32), 0 + 1*16 + 1*16 + 1*5(37), 0 + 1*16 + 1*16 + 2*5(42), 0 + 1*16 + 1*16 + 3*5(47)
gslice defines following members.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| gslice(size_t start, valarray<size_t> size, valarray<size_t> stride) | Constructor |
| size_t start() | returns start. |
| valarray<size_t> size() | returns size. |
| valarray<size_t> stride() | returns stride. |
gslice_array
Represents an intermediate type returned by valarray's subscript operator (operator[]) when used with gslices.
It references the elements in the valarray object that are selected by the gslice, and overloads the assignment and compound assignment operators, allowing direct access to the elements in the selection.
The type is convertible to a valarray, producing a new object with copies of the referred elements.
The following members are defined.
template <class T> class gslice_array { public: typedef T value_type; void operator= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator*= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator/= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator%= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator+= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator-= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator^= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator&= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator|= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator<<= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator>>= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator=(const T&) const; gslice_array() = delete; gslice_array(const gslice_array&); const gslice_array& operator= (const gslice_array&) const; ~gslice_array(); };
The following diagram depicts slice and gslice_array pictorially.
The following examples demonstrates getting diagonal elements in a 3D 4x4 matrix.
valarray<int> m(4*4*3); int n = 0; for (auto i=0; i<3; ++i) for (auto k=0; k<4; ++k) for (auto j=0; j<4; ++j) m[n++]=(k+1)*100+(j+1)*10+(i+1);//m:{111 121 131 141 211 221 231 241 311 321 331 341 411 421 431 441}//m:{112 122 132 142 212 222 232 242 312 322 332 342 412 422 432 442}auto d = valarray(m[gslice(0,{3,1,4},{16,16,5})]);//m:{113 123 133 143 213 223 233 243 313 323 333 343 413 423 433 443 }//d:{111 221 331 441 112 222 332 442 113 223 333 443}
mask_array
Represents an intermd="mask_array"ediate type returned by valarray's subscript operator (operator[]) when used with masks.
It references the elements in the valarray object that are selected by the an array of masks stored in a valarray<bool> and overloads the assignment and compound assignment operators, allowing direct access to the elements in the selection.
The type is convertible to a valarray, producing a new object with copies of the referred elements.
The following members are defined.
template <class T> class mask_array { public: typedef T value_type; void operator= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator*= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator/= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator%= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator+= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator-= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator^= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator&= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator|= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator<<= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator>>= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator=(const T&) const; mask_array() = delete; mask_array(const mask_array&); const mask_array& operator= (const mask_array&) const; ~mask_array(); };
The following diagram depicts mask_array pictorially.

The following examples returns values in even indices.
valarray<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; valarray<bool> m{1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0}; //odd:1 3 5 7 9 auto odd = valarray(v[m]);
indirect_array
Represents an intermediate type returned by valarray's subscript operator (operator[]) when used with indices.
It references the elements in the valarray object that are selected by the an array of indices stored in a valarray<size_t> and overloads the assignment and compound assignment operators, allowing direct access to the elements in the selection.
The type is convertible to a valarray, producing a new object with copies of the referred elements.
The following members are defined.
template <class T> class indirect_array { public: typedef T value_type; void operator= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator*= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator/= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator%= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator+= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator-= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator^= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator&= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator|= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator<<= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator>>= (const valarray<T>&) const; void operator=(const T&); indirect_array() = delete; indirect_array(const gslice_array&); const indirect_array& operator= (const indirect_array&) const; ~indirect_array(); };
The following diagram depicts indirect_array pictorially.
The following examples returns values in odd indices.
valarray<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; valarray<size_t> i{1,3,5,6,9}; //even:2 4 6 7 10 auto even = valarray(v[i]);